Understanding GSM Network: A Comprehensive Guide
The GSM network, or Global System for Mobile Communications, is one of the most widely used mobile communication technologies in the world today. This technology has revolutionized the way we communicate, allowing seamless voice calls, messaging, and mobile internet access. In this article, we will dive deep into the GSM network, exploring its history, functionality, components, and its impact on modern communication. Whether you are a telecommunications professional, a student, or just curious about how mobile networks operate, this guide will equip you with valuable insights.
The GSM network was developed in the 1980s and has since evolved to support a wide range of services. The importance of GSM cannot be overstated, as it laid the foundation for subsequent mobile technologies, such as UMTS and LTE. With over 5 billion connections worldwide, understanding GSM is essential for anyone interested in the telecommunications industry.
In this article, we will cover various aspects of the GSM network, including its architecture, protocols, and security measures. Additionally, we will discuss the future of GSM technology and its relevance in the era of 5G. So, let’s embark on this informative journey to explore the world of GSM networks!
Table of Contents
- 1. History of GSM Network
- 2. Architecture of the GSM Network
- 3. GSM Network Protocols
- 4. Security in GSM Networks
- 5. Advantages of GSM Network
- 6. Disadvantages of GSM Network
- 7. The Future of GSM Technology
- 8. Conclusion
1. History of GSM Network
The GSM network was first conceptualized in the early 1980s by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). The goal was to create a standardized mobile communication system that could operate across different countries and networks. The first GSM call was made in 1991, marking a significant milestone in telecommunications history.
Over the years, GSM technology has undergone numerous upgrades to improve its capacity, speed, and security. The initial version was primarily focused on voice communication, but with the advent of mobile data services, GSM has evolved to support SMS, MMS, and mobile internet access.
2. Architecture of the GSM Network
The architecture of the GSM network is composed of several key components that work together to facilitate mobile communication. Understanding this architecture is crucial for grasping how GSM operates.
2.1 Components of GSM Network
- Mobile Station (MS): The user's device, such as a mobile phone or tablet.
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS): Comprises the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) and Base Station Controller (BSC), handling the radio communication with mobile stations.
- Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS): Manages call routing and mobility management, consisting of the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), Home Location Register (HLR), and Visitor Location Register (VLR).
- Operation Support System (OSS): Provides maintenance and management support for the GSM network.
2.2 Functions of Each Component
Each component of the GSM network has specific functions:
- Mobile Station (MS): Initiates and receives calls and messages, and provides user interfaces.
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS): Facilitates radio communication between the mobile station and the network.
- Base Station Controller (BSC): Manages multiple BTSs, handling radio resource allocation and handovers.
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC): Connects calls and manages call routing.
- Home Location Register (HLR): Stores user data and subscription information.
- Visitor Location Register (VLR): Temporarily stores user information for mobile stations currently in the MSC's area.
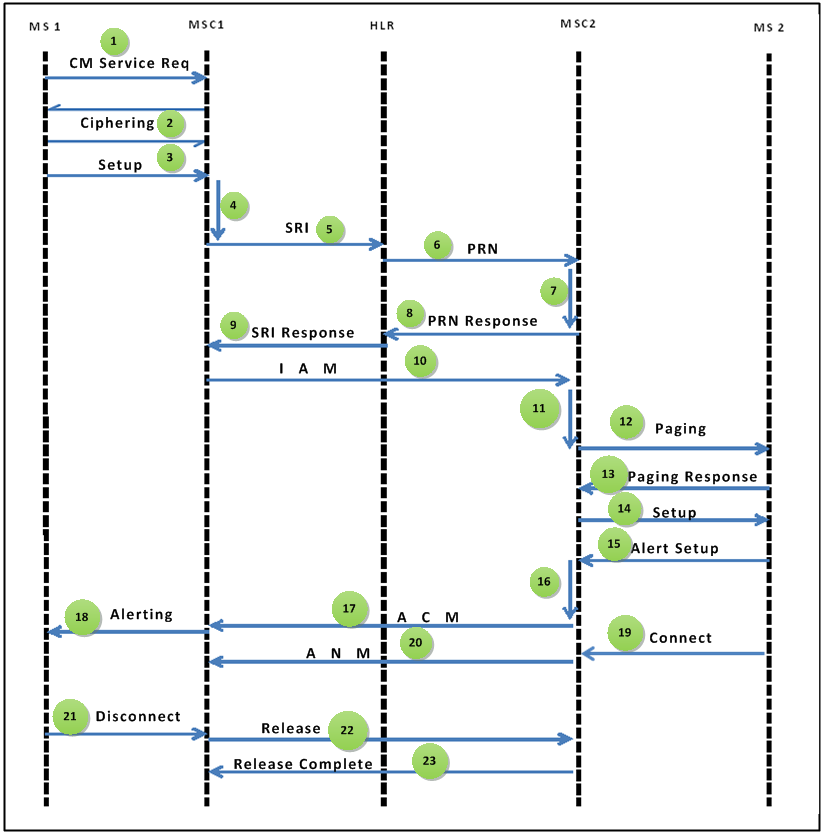
3. GSM Network Protocols
The GSM network relies on a set of protocols to ensure reliable communication. These protocols govern various aspects of mobile communication, such as call setup, data transfer, and security. Some key protocols include:
- Layered Architecture: GSM protocols follow a layered architecture, including the physical layer, data link layer, and network layer.
- Signaling System No. 7 (SS7): A protocol suite used for setting up and managing calls in a GSM network.
- Mobile Application Part (MAP): Facilitates communication between network elements, particularly related to user mobility.
4. Security in GSM Networks
Security is a critical aspect of GSM networks, as mobile communication involves sensitive information. GSM employs several security measures to protect user data:
- Encryption: GSM uses encryption algorithms to secure voice and data transmissions.
- Authentication: A robust authentication process ensures that only authorized users can access the network.
- Subscriber Identity Module (SIM): The SIM card stores user credentials and encryption keys, adding an additional layer of security.
5. Advantages of GSM Network
The GSM network offers several advantages that have contributed to its widespread adoption:
- International Roaming: GSM networks allow users to roam internationally, enabling seamless communication across borders.
- Wide Availability: With a vast infrastructure, GSM is available in most countries, making it accessible to millions.
- Support for Data Services: GSM supports SMS, MMS, and mobile internet, enhancing user experience.
6. Disadvantages of GSM Network
Despite its advantages, GSM networks have certain limitations:
- Data Speed: Compared to newer technologies like LTE, GSM's data transfer speeds are relatively low.
- Limited Capacity: GSM networks can experience congestion during peak usage times.
7. The Future of GSM Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of GSM networks is also changing. While GSM will remain relevant for many years, the rise of 3G, 4G, and 5G networks is reshaping the landscape. Many operators are gradually phasing out their GSM services in favor of more advanced technologies that offer faster data speeds and improved capabilities.
However, GSM technology will continue to play a crucial role in supporting IoT applications and rural connectivity, where newer technologies may not yet be available.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the GSM network has significantly impacted the telecommunications industry, providing a reliable and standardized mobile communication system. Understanding its architecture, protocols, and security measures is essential for anyone interested in mobile communications.
We encourage you to leave your comments below, share this article with others, or explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of mobile technologies.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to welcoming you back to our site for more insightful content!
Noel Gugliemi Net Worth: An In-Depth Look At His Wealth And Career
Is Michael Keaton Married? Exploring The Actor's Personal Life
Adam Harrison: The Journey Of Rick Harrison's Son